Orthopedics
Editor's pick
Research Article
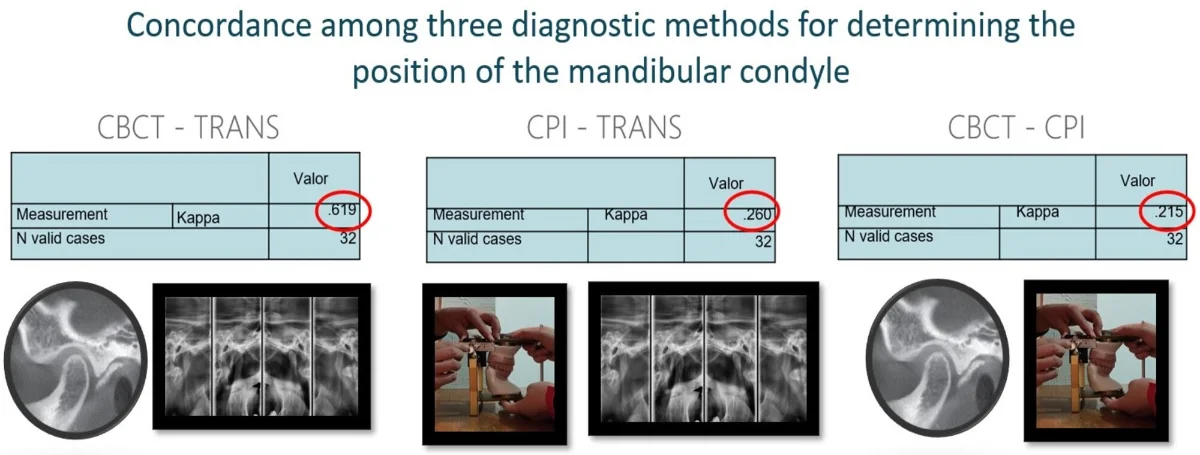
Concordance among three diagnostic methods for determining the position of the mandibular condyle
By Aidé Terán, Alejandro Liévano, Elia Núñez, Héctor Ruíz, Verónica Cabeza, Alejandro Lloret, Miguel Lloret
The position of the condyle can be determined using different diagnostic tools, among which are transcranial X-rays (RT), Cone Beam Computed Tomography (CBCT), and the Condylar Position Indicator (CPI). This study aimed to determine the concordance among the CPI, the CBCT, and the RT as diagnostic methods for determining the condyle position. Materials and method: 32 valid cases, each of which had an RT, a CBCT, and a CPI, were analyzed by three observers. SPSS V. 26.0 program was used to calculate the Kappa trust interval, using the jackknife technique which allows to estimate of the standard error between observers. To evaluate the condylar position using CPI, an AD2 articulator was employed. A Pullinger and Hollender layout was used in the tomographic and transcranial images. Results: The concordance among the three observers for each method resulted in a value of Kappa higher than 0.879. The concordance between CBCT and RT was 0.0627, between CPI and RT it was 0.247, and between CBCT and CPI it was .188. Conclusion: The level of concordance obtained between the three observers with any given diagnostic method was very good, which indicates that the concordance that each observer obtained regarding each diagnostic method is trustworthy. In this study, it is concluded that there is a concordance in the diagnosis regarding the position of the condyle of the tomography with the transcranial radiography. There is no concordance between tomography and CPI. There was also no concordance between the CPI and the transcranial radiography.
November 13, 2023
Orthopedics
Most cited
Research Article
Treatment of temporomandibular dysfunction with jaw functional orthopedics: a retrospective study
By Orlando Santiago Júnior, Marcus Vinicius Lucas Ferreira, Rudolf Huebner
June 21, 2021
Orthopedics
Most cited
Research Article
Effects of mechanical vibration on bone – a critical review
By Orlando Santiago Júnior, Rudolf Huebner, Maria Lucia Duarte
November 28, 2022
Orthopedics
Most cited
Research Article
Functional orthopedic appliance for vertical dimension increase and mandibular deprogramming ORLANDO SANTIAGO SYSTEM 1 – OSS1. Indications and laboratorial manufacturing
By Orlando Santiago Júnior, Mario Vedovello Filho, Marcus Vinicius Lucas Ferreira, Rudolf Huebner
June 22, 2021
Orthopedics
Most cited
Research Article
Does Planas’ Equiplan really work in deep bite treatment?
By Orlando Santiago Júnior
December 29, 2021
Orthopedics
Jaw Functional Orthopedics and Craniofacial Growth
Research Article
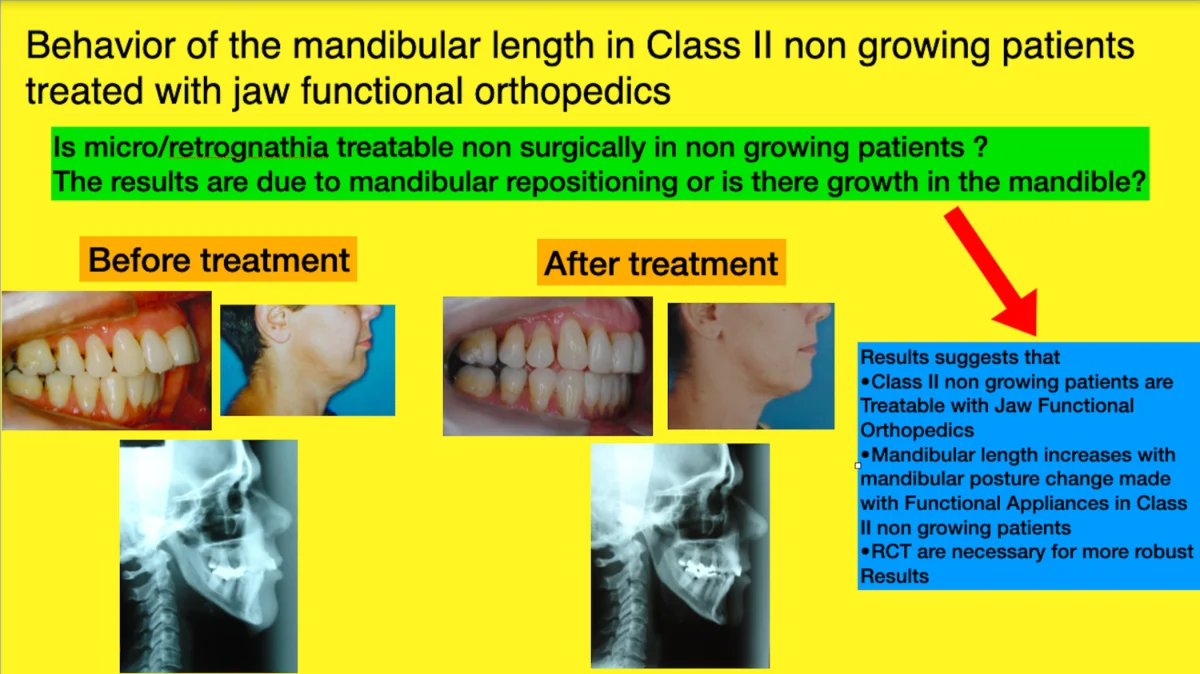
Behavior of the mandibular length in class II non-growing patients treated with jaw functional orthopedics
Class II treatment is the leader of seeking for dentofacial correction in offices all around the world due, mainly, to facial esthetics impairment caused by this malocclusion. Mandibular forward repositioned is needed for the majority of this treatment. Jaw Functional Orthopedics (JFO) is a recognized protocol to treat Class II in growing patients. The aim of this investigation is to study the behavior of mandibular length in class II non-growing patients treated with JFO. Distance between Gonion and Mento were measured in lateral teleradiographs at T0 and T1 (from 18 to 21 months of treatment) of non-growing class II patients under treatment with JFO and mandibular supplementary growth was found (P = 0,006). In the sample studied jaw functional orthopedics showed to be efficient to correct the overjet in class II non-growing patients. Mandibular advancement with functional orthopedic appliances promotes a supplementary mandibular growth in non-growing patients. Further studies are necessary for a better comprehension of the subject.
December 27, 2022
Orthopedics

Research Article
Planas direct tracks to treat functional crossbites in children: scientific evidence
Introduction: Posterior functional crossbite is a common malocclusion in children, with a prevalence between 7.5-24 %. It has an important impact on facial functions, and may cause asymmetries in craniofacial development. Different interventions have been used to correct this malocclusion but there is a lack of studies with methodological rigor that support these interventions. Planas Direct Tracks (PDT) constitute one of such interventions. They seek to reestablish the functional occlusal balance of children through selective grinding, complementing this adjustment with composites. Objective: To present the level of scientific evidence available on PDT to correct posterior crossbites. Method: A sensitive search was carried out in the main databases: Pubmed, BVS Odontology, Cochrane, SciElo and Google academic. The articles were selected, duplications removed and critical evaluation of the literature performed classifying the studies according to the evidence pyramid. The aim is to point out ways to improve the quality of the studies. Results: 32 studies were included. 30 studies were narrative reviews, case reports or case series and two were controlled trials. All studies had important biases. No randomized controlled trial was found. Conclusion: So far, there are no studies, sufficiently rigorous methodology, on Planas direct tracks to correct functional crossbites.
November 1, 2022
Orthopedics
Research Article
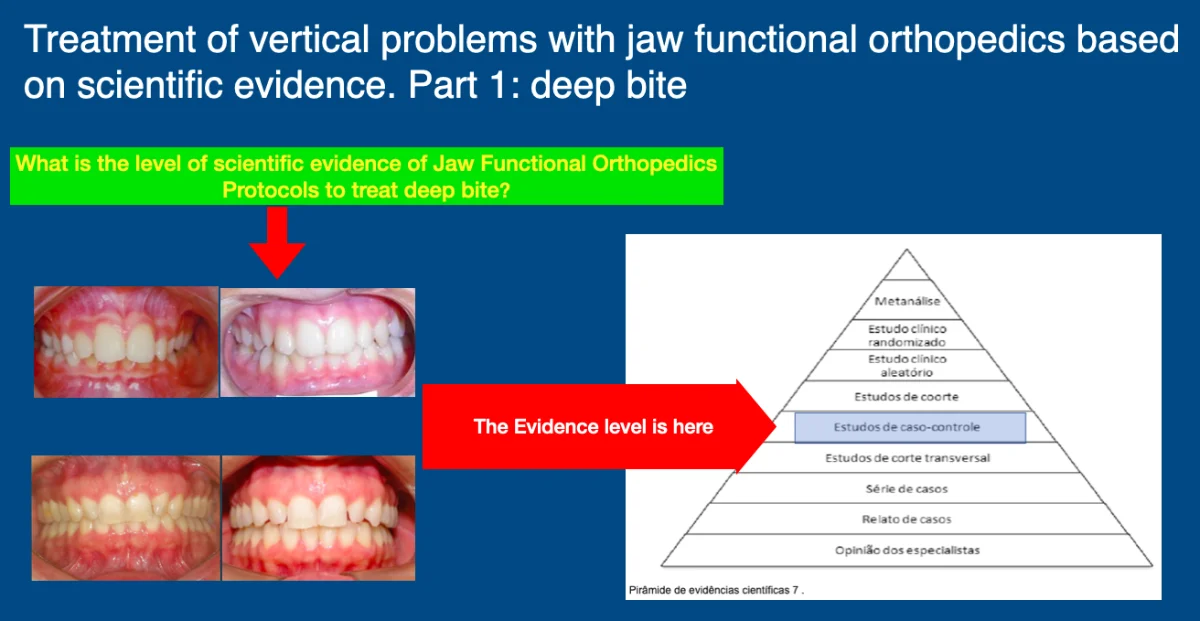
Treatment of vertical problems with jaw functional orthopedics based on scientific evidence. Part 2: deep bite
The vertical problems of the stomatognathic system that alter the overbite, either by increasing in the deep bite (DB) or decreasing in the anterior open bite (AOB), are among the great challenges of the dentofacial corrections in the treatment and the retention and stability protocols. In this paper the state of art of DB treatment with Jaw Functional Orthopedics (JFO) will be discussed. JFO has a unique diagnostic tool for changes in vertical growth of the face, the Articular Compass, developed by Simões. Individuals with hypodivergence and DB are, usually, difficult to treat and more difficult to stabilize the obtained results. Since 1950-decade Planas advocate that the Equiplan – a metal accessory used in functional orthopedic appliances (FOA) is efficient in deep bite treatment by levelling the occlusal plane. Promising results are found with a P = 0,00, but in aweak evidence study design based on the scientific evidence pyramid. Much of the discussion of incisor intrusion or molar extrusion to treat DB seems to be solved with the use of Equiplan, but it still has no scientific evidence, only clinical evidence. In conclusion Randomized Clinical Trials are needed to investigate the efficiency and Modus Operandi of JFO to treat DB.
November 1, 2022
Orthopedics
Research Article
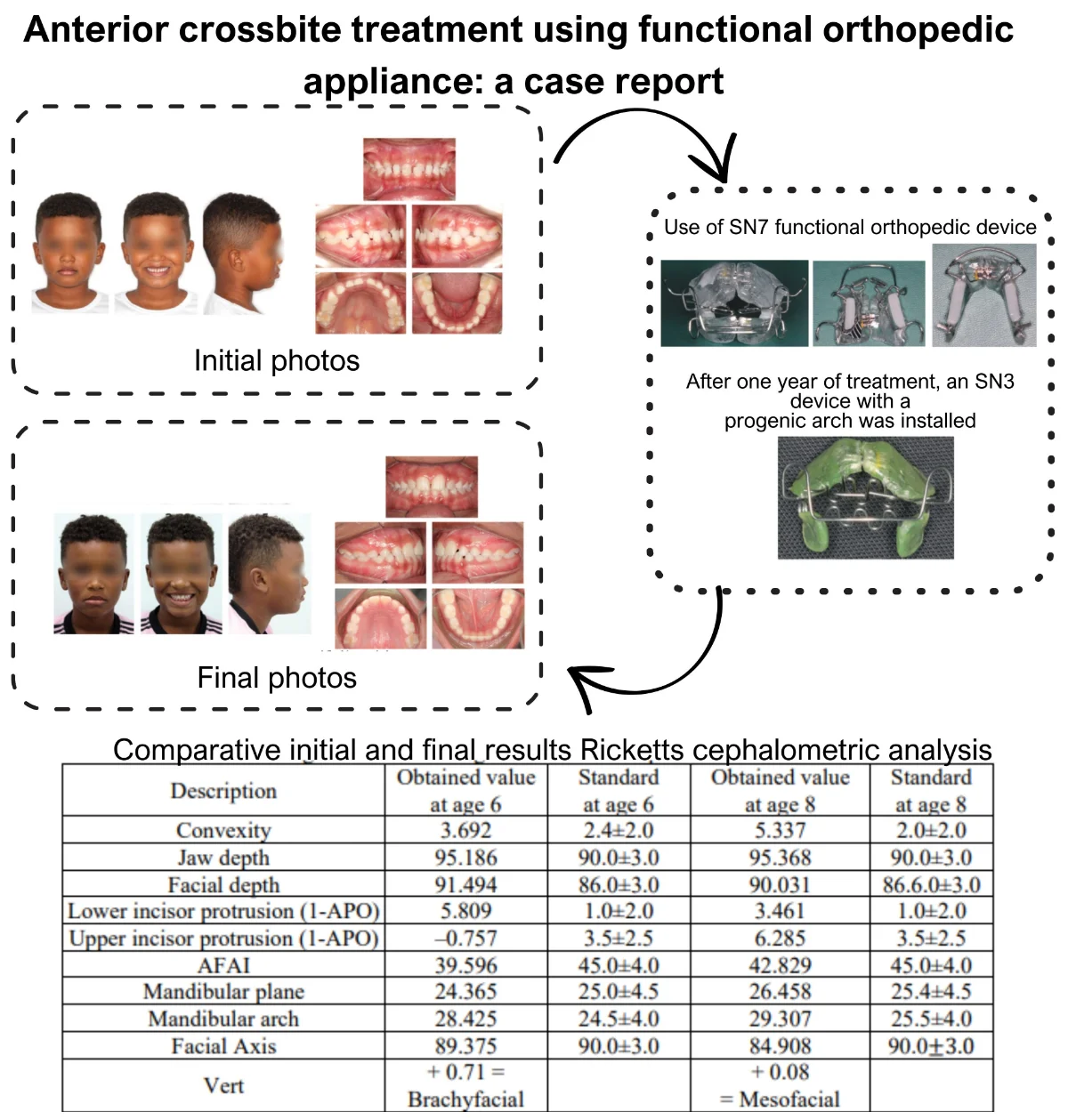
Anterior crossbite treatment using functional orthopedic appliance: a case report
Anterior crossbite can affect primary, mixed, and permanent dentitions. Early treatment is recommended, as it can impact facial, aesthetic, functional, and developmental aspects. The etiology of anterior crossbite is multifactorial, including dental, skeletal, and postural origins. Treatment should be defined based on age and etiology, with various therapeutic resources available for correction. In primary dentition, direct flat tracks, different types of functional orthopedic appliances, quad-helix, and facial mask can be used. In mixed dentition, fixed segmented or continuous orthodontics, elastics, and other devices can be added to the treatment. In permanent dentition, orthognathic surgery may be indicated for adults, especially in cases of anterior crossbite associated with skeletal Class III that cannot be compensated dentally. This case report describes the treatment of early mixed dentition anterior crossbite with a functional orthopedic appliance at the Orthodontic Specialization, Postgraduate Course at Modal college, Belo Horizonte, Minas Gerais, Brazil. After correction, proper chewing functions were reestablished with ideal developmental stimuli.
June 28, 2023
Orthopedics
Jaw Functional Orthopedics and Craniofacial Growth
Original scientific articles presenting information that is new and relevant to jaw functional orthopedics
APC
Free of charge
Best of Theme
Most cited
Research article
November 1, 2022
Functional orthopedic device type Sn20 – a therapeutic resource in the control of chronic temporomandibular dysfunction – case report
By C. A. O. Machado, P.-C. Simamoto Junior
Most cited
Research article
June 30, 2022
Occlusal plane parallel to camper plane: reality or fallacy? A tomographic study on human Sambaqui skeletal remains
By Patrícia Valério, Maria Rita Xavier, Sergio Terçaroli, Almiro Machado, Marcos Gribel
Most cited
Research article
November 1, 2022
Treatment of vertical problems with jaw functional orthopedics based on scientific evidence. Part 1: anterior open bite
By Orlando Santiago Júnior
Most cited
Research article
November 1, 2022
Corporeal-composition indicators, and physiological alterations in dental eruption
By Miguel Francisco Javier Lloret Rivas, Claudia Ariana Olamendi Pérez, Héctor Mancilla Herrera, Aidé Terán Alcocer
You might also like
Most downloaded
Research Article
Treatment of traumatic facial paralysis with mechanical stimulus – hyperboloid: case report
By Fabiana Augusto Novo Borghi, Rosana Queiroz, José Ricardo Gurgel Testa
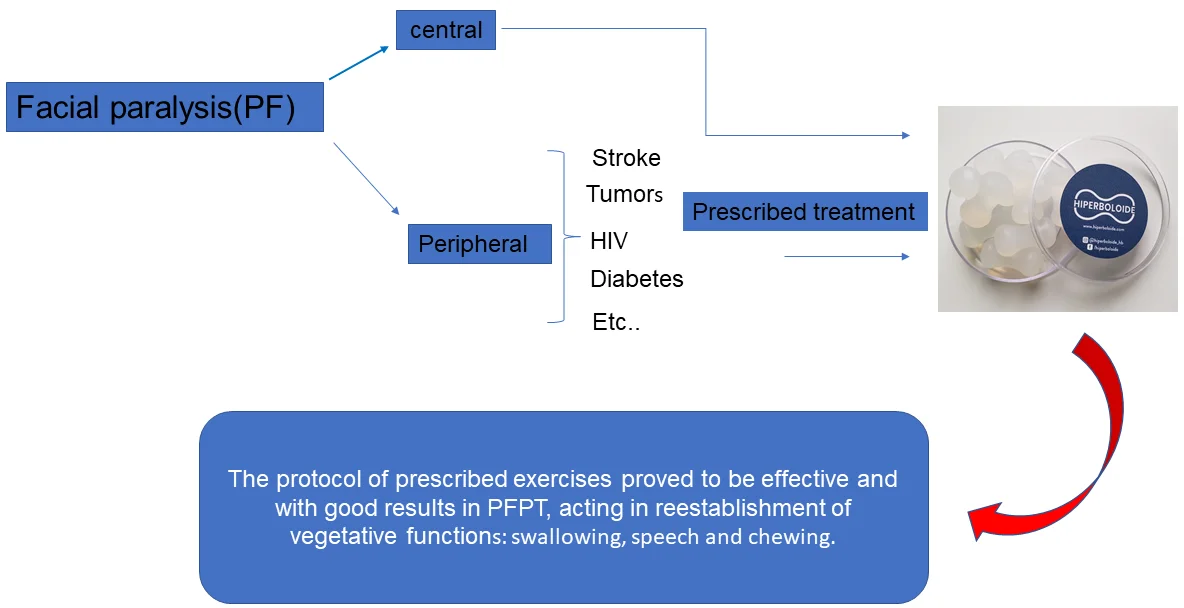
Paralysis is the complete abolition of movement in a given territory of the body. Traumatic peripheral facial paralysis (PFPT) is characterized by lack of movement, due to injuries to the seventh cranial nerve (Facial Nerve), as a result of surgical resection of tumors in the region, firearm trauma, falls etc., can be uni or bilateral. Individuals affected by this paralysis when unilateral, tend to present facial asymmetry between the hemi faces, both at rest and in movement, as well as functional limitations to perform activities such as drinking, eating, speaking and problems in ocular hydration (dryness or watery eyes). In the case report, the patient underwent several types of treatment with very limited results. After 30 days of therapy with the hyperboloid, the patient reported improvements in clinical and motor conditions.
September 13, 2021
Orthopedics
Most downloaded
Research Article
Clinical application of digitalization of occlusal contacts with dental scanner
By Janet Guevara Reyes
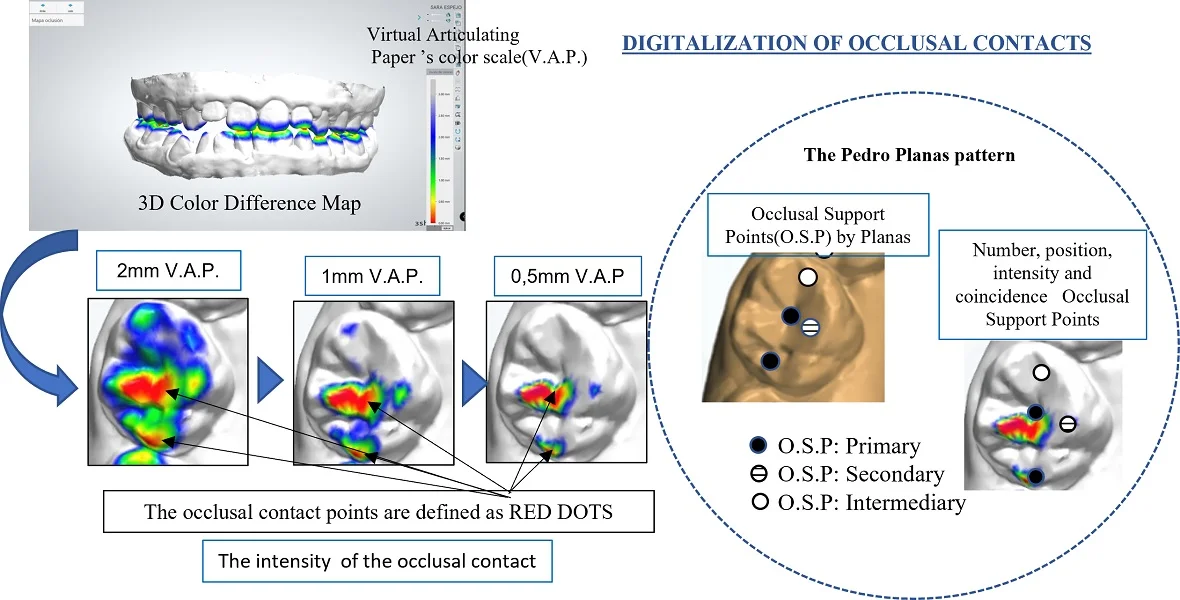
This study aimed to evaluate the number, intensity and position of occlusal contact points in a case of mesiocclusion, hyperdivergence, with open bite. An occlusal record was taken from a patient with anterior and lateral open bite mesiocclusion, using the Planmeca Esmerald S intraoral scanner in maximum intercuspation. The intensity of the occlusal contact was analyzed with the software 3shape Ortho Analyzer Orthodontics, using the Occlusion Map module, through the 3D Color Map tool, with a 0.5 mm virtual articular paper. These results were compared to the occlusal support points defined by Planas [10]. The interpretation of the data obtained was made by assessing the interocclusal intensity of the contact points, number of contacts and position during three different moments (1S, 2S, 3S) in the record taking process. The chromatic scale of the Color Map is: red, orange, yellow, green and blue. To identify the occlusal contact points in digital, they are shown in red points when full contact occurs, while minimum contact is shown in blue. We evaluated the number of teeth with interocclusal contacts. It was determined that having the appropriate number of contacts does not imply that they are in the correct position. In addition, the method suggests reliability in the filing and record keeping of occlusal contacts. By identifying intensity, number and position of the occlusal support point we can objectively record interocclusal alterations.
November 1, 2022
Orthopedics
Simões Network 2 (SN2): A special model for special needing
Functional Orthopedics appliances must follow strict rules of construction and respect the correct indications, to achieve the proposed goals. The approach must be individualized for each patient according to each needing. Dr Wilma Alexandre Simões created a network of appliances, with no similarity with other appliances created by other authors. Her appliances respect rigid scientific fundamentals and provide for the clinician special tools for solving different types of occlusopathies. Here we present some rules, developed, and scientifically supported by the authors, in order to optimize the use of one of Simões Network called SN2.
Prevalence of orofacial pain and temporomandibular disorder among violin and viola players: a pilot study
Prevalence of orofacial pain and temporomandibular disorder was evaluated among violin and viola players, having as control group other string players (cello and double base players). We found a high prevalence and more severity on violin /viola players. We also found that it is not related to the number of hours performing the instruments. Violin and viola players are more prone to headache and more aware of their parafunctional behavior.